Tech & IT
Tech & IT
 Business
Business
 Coding & Developer
Coding & Developer
 Finance & Accounting
Finance & Accounting
 Academics
Academics
 Office Applications
Office Applications
 Art & Design
Art & Design
 Marketing
Marketing
 Health & Wellness
Health & Wellness
 Sounds & Music
Sounds & Music
 Lifestyle
Lifestyle
 Photography
Photography
More Learnfly
Business Solution Become an InstructorRadio frequency (RF) refers to the oscillation rate of electromagnetic waves in the radio wave frequency range. Widely used in communication, RF technology enables wireless devices, including radios and smartphones, facilitating data transmission, broadcasting, and various applications in telecommunications and technology.












Learn more topics in various categories at one place. Explore unlimited courses in other categories and up-skill yourself today.

 Jazeb Akram
Jazeb Akram 4.2 771159 Beginner Level

 John Hedengren
John Hedengren 4.1 569062 All Level
 Ranjan Pandey
Ranjan Pandey 4.1 346728 All Level

 Muhammad Ahsan Pervaiz
Muhammad Ahsan Pervaiz 4.2 101337 All Level

 Pieter Vliegenthart
Pieter Vliegenthart 4.6 100916 All Level

 Jerome P.
Jerome P. 4.8 100881 All Level

 Senol Atac
Senol Atac 4.9 100091 All Level

 Vikas Munjal
Vikas Munjal 4.8 100064 Beginner Level

 Avinash A
Avinash A 4.8 100013 All Level

 ExpertEase Education
ExpertEase Education20 Lectures

 Kiran Beldar
Kiran Beldar21 Lectures
 Bazeer Ahamed Mohamed Nishad
Bazeer Ahamed Mohamed Nishad14 Lectures
.jpg)
 Naman kumar Gandhi
Naman kumar Gandhi 8 Lectures
.jpg)
 Naman kumar Gandhi
Naman kumar Gandhi 24 Lectures

 Nour ElAkhdar
Nour ElAkhdar18 Lectures

 Nour ElAkhdar
Nour ElAkhdar12 Lectures
.png)
 Nour ElAkhdar
Nour ElAkhdar19 Lectures

 Nour ElAkhdar
Nour ElAkhdar14 Lectures

 Dr. Kiran Derle
Dr. Kiran Derle29 Lectures

 Dr. Kiran Derle
Dr. Kiran Derle55 Lectures

 Shivkumar Iyer
Shivkumar Iyer8 Lectures

 Edu Mark India
Edu Mark India30 Lectures

 MUSTAFA VARICI
MUSTAFA VARICI80 Lectures

 MUSTAFA VARICI
MUSTAFA VARICI58 Lectures
 Gilad James, PhD
Gilad James, PhD31 Lectures

 Gilad James, PhD
Gilad James, PhD17 Lectures

 MUSTAFA VARICI
MUSTAFA VARICI76 Lectures
 Krunal Shah
Krunal Shah26 Lectures

 John Peterson
John Peterson6 Lectures

 Taimor Khan
Taimor Khan68 Lectures

 Sumit Saha (Ph.D)
Sumit Saha (Ph.D)105 Lectures
 Dwijaraja Gore
Dwijaraja Gore17 Lectures

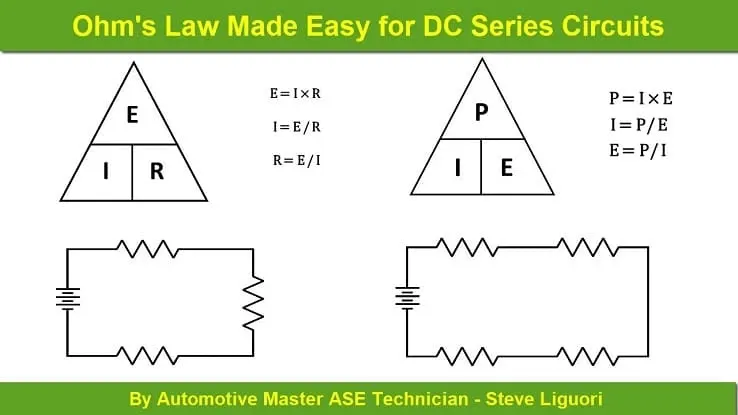
 Steve Liguori
Steve Liguori25 Lectures
 Steve Liguori
Steve Liguori25 Lectures

 Salih Zinaty
Salih Zinaty66 Lectures

 Elite Education
Elite Education6 Lectures

 Ziad Baraka
Ziad Baraka33 Lectures
Radio Frequency (RF) refers to the range of electromagnetic frequencies used for various wireless communications, including radio broadcasting, television, mobile networks, Wi-Fi, and satellite communications. RF signals encompass a range of frequencies from a few kilohertz to hundreds of gigahertz.
RF is vital for wireless communication technologies, allowing the transmission of data and information over the airwaves. It enables various applications, including broadcasting, mobile and satellite communication, radar systems, and wireless networking.
Main applications include radio broadcasting, television transmission, mobile communication (cellular networks), satellite communication, radar systems, RFID (Radio Frequency Identification), and various wireless technologies like Wi-Fi and Bluetooth.
RF technology involves the generation of electromagnetic waves within the radio frequency spectrum. Transmitters convert electrical signals into RF waves, which can then be received by antennas and converted back into electrical signals. Modulation techniques are used to encode information onto the RF carrier wave.
Challenges include interference from other RF signals, signal attenuation over distance, and susceptibility to environmental conditions. RF engineers must consider factors like frequency allocation, bandwidth, and signal strength to optimize communication and minimize potential issues.