Tech & IT
Tech & IT
 Business
Business
 Coding & Developer
Coding & Developer
 Finance & Accounting
Finance & Accounting
 Academics
Academics
 Office Applications
Office Applications
 Art & Design
Art & Design
 Marketing
Marketing
 Health & Wellness
Health & Wellness
 Sounds & Music
Sounds & Music
 Lifestyle
Lifestyle
 Photography
Photography
More Learnfly
Business Solution Become an InstructorSolar energy utilizes sunlight for electricity and heat, employing photovoltaic cells and solar thermal systems. As a renewable source, it reduces reliance on non-renewable energy, fostering environmental sustainability.












Learn more topics in various categories at one place. Explore unlimited courses in other categories and up-skill yourself today.

 Jazeb Akram
Jazeb Akram 4.2 771159 Beginner Level

 John Hedengren
John Hedengren 4.1 569062 All Level
 Ranjan Pandey
Ranjan Pandey 4.1 346728 All Level

 Muhammad Ahsan Pervaiz
Muhammad Ahsan Pervaiz 4.2 101337 All Level

 Pieter Vliegenthart
Pieter Vliegenthart 4.6 100916 All Level

 Jerome P.
Jerome P. 4.8 100881 All Level

 Senol Atac
Senol Atac 4.9 100091 All Level

 Vikas Munjal
Vikas Munjal 4.8 100064 Beginner Level

 Avinash A
Avinash A 4.8 100013 All Level

 ExpertEase Education
ExpertEase Education20 Lectures

 Kiran Beldar
Kiran Beldar21 Lectures
 Bazeer Ahamed Mohamed Nishad
Bazeer Ahamed Mohamed Nishad14 Lectures
.jpg)
 Naman kumar Gandhi
Naman kumar Gandhi 8 Lectures
.jpg)
 Naman kumar Gandhi
Naman kumar Gandhi 24 Lectures

 Nour ElAkhdar
Nour ElAkhdar18 Lectures

 Nour ElAkhdar
Nour ElAkhdar12 Lectures
.png)
 Nour ElAkhdar
Nour ElAkhdar19 Lectures

 Nour ElAkhdar
Nour ElAkhdar14 Lectures

 Dr. Kiran Derle
Dr. Kiran Derle29 Lectures

 Dr. Kiran Derle
Dr. Kiran Derle55 Lectures

 Shivkumar Iyer
Shivkumar Iyer8 Lectures

 Edu Mark India
Edu Mark India30 Lectures

 MUSTAFA VARICI
MUSTAFA VARICI80 Lectures

 MUSTAFA VARICI
MUSTAFA VARICI58 Lectures
 Gilad James, PhD
Gilad James, PhD31 Lectures

 Gilad James, PhD
Gilad James, PhD17 Lectures

 MUSTAFA VARICI
MUSTAFA VARICI76 Lectures
 Krunal Shah
Krunal Shah26 Lectures

 John Peterson
John Peterson6 Lectures

 Taimor Khan
Taimor Khan68 Lectures

 Sumit Saha (Ph.D)
Sumit Saha (Ph.D)105 Lectures
 Dwijaraja Gore
Dwijaraja Gore17 Lectures

 Steve Liguori
Steve Liguori25 Lectures
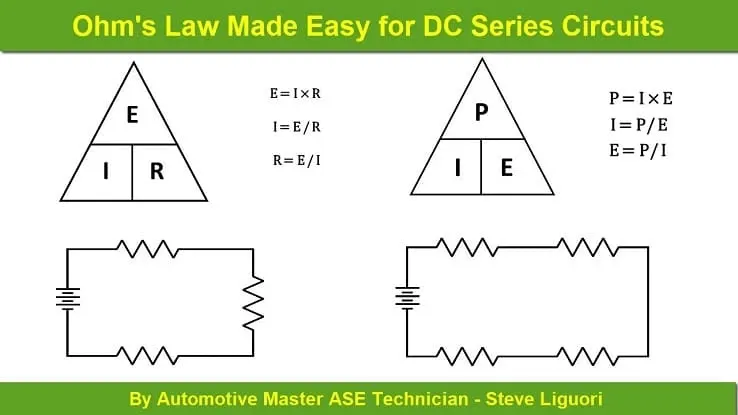
 Steve Liguori
Steve Liguori25 Lectures

 Salih Zinaty
Salih Zinaty66 Lectures

 Elite Education
Elite Education6 Lectures

 Ziad Baraka
Ziad Baraka33 Lectures
Solar energy is a renewable and sustainable form of energy derived from the sun's radiation. It can be harnessed using various technologies to generate electricity, heat water, and power various applications, contributing to a cleaner and more environmentally friendly energy source.
Solar energy is important for its environmental benefits, as it is a clean and abundant source of power. It reduces reliance on fossil fuels, decreases greenhouse gas emissions, and contributes to addressing climate change. Solar power is also becoming economically competitive.
Main technologies include photovoltaic (PV) systems, which convert sunlight into electricity using solar cells, and solar thermal systems, which use sunlight to generate heat for water heating or electricity generation. Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) is another technology that focuses sunlight to produce high-temperature heat.
Solar energy has a minimal environmental impact compared to conventional energy sources. It reduces air pollution, water usage, and carbon dioxide emissions. However, the production and disposal of solar panels do have environmental considerations that need to be managed.
Challenges include intermittency (dependence on sunlight), energy storage solutions, and the need for efficient and cost-effective technologies. Advancements in solar cell efficiency, energy storage systems, and innovations in manufacturing processes are addressing these challenges, making solar energy more viable and widespread.