



 Tech & IT
Tech & IT
 Business
Business
 Coding & Developer
Coding & Developer
 Finance & Accounting
Finance & Accounting
 Academics
Academics
 Office Applications
Office Applications
 Art & Design
Art & Design
 Marketing
Marketing
 Health & Wellness
Health & Wellness
 Sounds & Music
Sounds & Music
 Lifestyle
Lifestyle
 Photography
Photography
More Learnfly
Business Solution Become an InstructorStatistics involves collecting, analyzing, interpreting, and presenting data. It provides methods for drawing meaningful conclusions from information, aiding decision-making in diverse fields such as science, business, and social sciences.












Learn more topics in various categories at one place. Explore unlimited courses in other categories and up-skill yourself today.

 Jazeb Akram
Jazeb Akram 4.2 771150 Beginner Level

 John Hedengren
John Hedengren 4.1 569054 All Level
 Ranjan Pandey
Ranjan Pandey 4.1 346720 All Level

 Muhammad Ahsan Pervaiz
Muhammad Ahsan Pervaiz 4.2 101327 All Level

 Pieter Vliegenthart
Pieter Vliegenthart 4.6 100908 All Level

 Jerome P.
Jerome P. 4.8 100869 All Level

 Senol Atac
Senol Atac 4.9 100082 All Level

 Vikas Munjal
Vikas Munjal 4.8 100059 Beginner Level

 Avinash A
Avinash A 4.8 100002 All Level

 ExpertEase Education
ExpertEase Education20 Lectures All Level

 Kiran Beldar
Kiran Beldar21 Lectures All Level
 Bazeer Ahamed Mohamed Nishad
Bazeer Ahamed Mohamed Nishad14 Lectures All Level
.jpg)
 Naman kumar Gandhi
Naman kumar Gandhi 8 Lectures All Level
.jpg)
 Naman kumar Gandhi
Naman kumar Gandhi 24 Lectures All Level

 Nour ElAkhdar
Nour ElAkhdar18 Lectures All Level

 Nour ElAkhdar
Nour ElAkhdar12 Lectures All Level
.png)
 Nour ElAkhdar
Nour ElAkhdar19 Lectures All Level

 Nour ElAkhdar
Nour ElAkhdar14 Lectures All Level

 Dr. Kiran Derle
Dr. Kiran Derle29 Lectures All Level

 Dr. Kiran Derle
Dr. Kiran Derle55 Lectures All Level

 Shivkumar Iyer
Shivkumar Iyer8 Lectures All Level

 Edu Mark India
Edu Mark India30 Lectures All Level

 MUSTAFA VARICI
MUSTAFA VARICI80 Lectures All Level

 MUSTAFA VARICI
MUSTAFA VARICI58 Lectures All Level
 Gilad James, PhD
Gilad James, PhD31 Lectures All Level

 Gilad James, PhD
Gilad James, PhD17 Lectures All Level

 MUSTAFA VARICI
MUSTAFA VARICI76 Lectures All Level
 Krunal Shah
Krunal Shah26 Lectures All Level

 John Peterson
John Peterson6 Lectures All Level

 Taimor Khan
Taimor Khan68 Lectures All Level

 Sumit Saha (Ph.D)
Sumit Saha (Ph.D)105 Lectures All Level
 Dwijaraja Gore
Dwijaraja Gore17 Lectures All Level

 Steve Liguori
Steve Liguori25 Lectures All Level
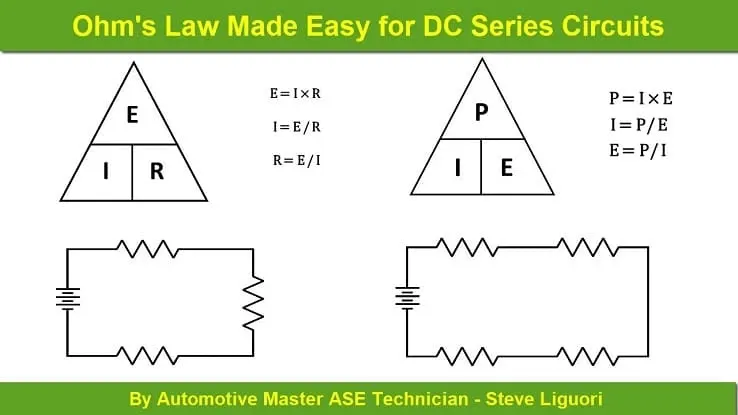
 Steve Liguori
Steve Liguori25 Lectures All Level

 Salih Zinaty
Salih Zinaty66 Lectures All Level

 Elite Education
Elite Education6 Lectures All Level

 Ziad Baraka
Ziad Baraka33 Lectures All Level
Statistics is a branch of mathematics that involves collecting, analyzing, interpreting, presenting, and organizing data. It provides methods for making inferences and drawing conclusions about populations based on samples, helping to understand and make sense of numerical information.
Statistics is important for drawing reliable conclusions from data, making informed decisions, and conducting research in various fields. It plays a crucial role in science, business, economics, and social sciences by providing tools for data analysis, hypothesis testing, and drawing meaningful insights.
Key concepts include descriptive statistics (summarizing and presenting data), inferential statistics (making predictions and inferences about populations based on samples), probability (likelihood of events), and hypothesis testing (making decisions about hypotheses based on data).
In scientific research, statistics is used to analyze experimental data, test hypotheses, and draw conclusions about the reliability of results. It helps researchers make meaningful interpretations and generalizations based on limited data.
Statistics is applied in various fields, including market research, epidemiology, finance, quality control, and social sciences. It is used to analyze trends, make predictions, assess risk, and guide decision-making in both academic and real-world contexts.





