This plan includes
- Limited free courses access
- Play & Pause Course Videos
- Video Recorded Lectures
- Learn on Mobile/PC/Tablet
- Quizzes and Real Projects
- Lifetime Course Certificate
- Email & Chat Support
What you'll learn?
- Learn Embedded C
- Learn how to program, use and interact with Arduino
- Learn how to program, use and interact with PIC Microcontroller
- Learn Communication Protocols
- Learn Circuit Design and Simulation from scratch
- Learn 3D Design and Simulation to make your own 3D Models
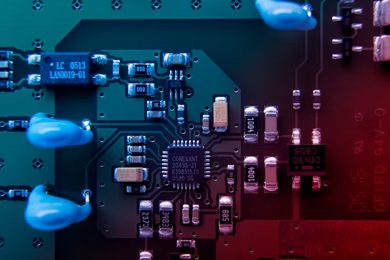
- Learn PCB Fabrication from scratch
- Learn everything about Embedded System
- Learn to use all the software tools needed to be successful as an Embedded System Engineer
- Build an Arduino prototype to create your own game using LEDs
- Learn how to solve complex problems with microcontrollers
- Learn how to make your own products - make them work!
- How to implement communication protocols in your project
Course Overview
Pre-requisites
- No prior experience in Embedded Systems is required
- You should have access to a Computer/laptop and Internet Connection
- You should be ready to commit 60 days to learning and practicing
- Be ready to Invent new things by making them do what you want
Target Audience
- Anyone who wants to QUICKLY learn how to become an embedded system engineer
- Geeks, University students, hobbyists who want to learn Embedded systems
- Anyone who wants to learn the entire embedded system product manufacturing process from beginning to end
- This is a special program for those who want to become an Embedded System Engineer
- Developers that wants to gain more knoweldge
- Developers that wants to gain more knoweldge
- Beginners
- Hobbyist
- Curious Learner
Curriculum 396 Lectures 42:21:31
Section 1 : Section 1
- Lecture 2 :
- Embedded System Introduction
- Lecture 3 :
- The Power of Search
- Lecture 4 :
- Download and Install C Editor and Compiler
- Lecture 5 :
- Write and Compile C Codes in your browser
- Lecture 6 :
- Download and Install Visual Studio Code To run C programs
- Lecture 7 :
- Write Your First C Code and Compile it
- Lecture 8 :
- Comments in C
- Lecture 9 :
- Strings and Escape characters in C
- Lecture 10 :
- Variables in C
Section 2 : Section 2
- Lecture 1 :
- Rules in naming variable in C
- Lecture 2 :
- Printing Variables with Printf in C
- Lecture 3 :
- Reading Input from User in C
- Lecture 4 :
- Arithmetic Operators in C
- Lecture 5 :
- Uni Arithmetic Operators in C
- Lecture 6 :
- Bitwise Operators in C
- Lecture 7 :
- Bitwise Shift Operators in C
- Lecture 8 :
- Assignment Operators
- Lecture 9 :
- Logical and Relational Operators
- Lecture 10 :
- Conditional Statement if in C
Section 3 : Section 3
- Lecture 1 :
- Conditional Statement else if and else in C
- Lecture 2 :
- General Rules Regarding if statement
- Lecture 3 :
- Conditional Statement - Switch
- Lecture 4 :
- Switch Statement General Rules in C
- Lecture 5 :
- For Loop in C
- Lecture 6 :
- Loops-While
- Lecture 7 :
- Do while Loops in C
- Lecture 8 :
- Break and Continue and C
- Lecture 9 :
- Functions in C
- Lecture 10 :
- Void Keyword in C
Section 4 : Section 4
- Lecture 1 :
- Local Variables and Global Variables in C
- Lecture 2 :
- Analog Input IR sensor
- Lecture 3 :
- What is Arduino Raspberry Pi and PIC Microcontroller
- Lecture 4 :
- Quick summary of the main differences
- Lecture 5 :
- Hardware IO Pins Storage and USB
- Lecture 6 :
- Software Comparison
- Lecture 7 :
- Expanding Onward Capabilities
- Lecture 8 :
- How to decide Which one
- Lecture 9 :
- Hardware Power and Connectivity
- Lecture 10 :
- Basic Parts Requirements
Section 5 : Section 5
- Lecture 1 :
- Parts needed to get the job done
- Lecture 2 :
- ATMEGA Introduction
- Lecture 3 :
- ATMEGA Connection
- Lecture 4 :
- Arduino Ready
- Lecture 5 :
- Boot-loading your chips optional
- Lecture 6 :
- Finish up and burn the bootloader
- Lecture 7 :
- How does it works
- Lecture 8 :
- Android Application
- Lecture 9 :
- Note
- Lecture 10 :
- Schematic
Section 6 : Section 6
- Lecture 1 :
- Code
- Lecture 2 :
- Testing Code
- Lecture 3 :
- Instruction
- Lecture 4 :
- What you will learn in this course
- Lecture 5 :
- What is Arduino + Software Download
- Lecture 6 :
- What is Ultrasonic Sensor
- Lecture 7 :
- What is Servo Motor
- Lecture 8 :
- Software Requirements Schematic
- Lecture 9 :
- Arduino Code Explained
- Lecture 10 :
- Processing Code + Java jdk
Section 7 : Section 7
- Lecture 1 :
- Basic Parts Needed for this Project
- Lecture 2 :
- Practical Assembly
- Lecture 3 :
- Software and Hardware Requirements
- Lecture 4 :
- How Does it Works
- Lecture 5 :
- Circuit Diagram
- Lecture 6 :
- Code Explained in Details
- Lecture 7 :
- Introduction for Arduino Weather Station
- Lecture 8 :
- Things Used in this Projects
- Lecture 9 :
- Things Used in this Project - Software and Web Editor
- Lecture 10 :
- Temperature and Humidity Sensor Wiring
Section 8 : Section 8
- Lecture 1 :
- Code to Test DHT Sensors using Serial Monitor
- Lecture 2 :
- Code for LCD and DHT Sensor Together
- Lecture 3 :
- Final Code for LCD RTC and DHT Sensor
- Lecture 4 :
- Required Materials
- Lecture 5 :
- Download and Install Arduino IDE
- Lecture 6 :
- Circuit Diagram LCD Connection Explained
- Lecture 7 :
- Circuit Diagram Continue
- Lecture 8 :
- How does it work
- Lecture 9 :
- Code Overview
- Lecture 10 :
- Code Explanation
Section 9 : Section 9
- Lecture 1 :
- How does it work
- Lecture 2 :
- Circuit Diagram
- Lecture 3 :
- Arduino Alarm Clock Code Part1
- Lecture 4 :
- Arduino Alarm Clock Code Part2
- Lecture 5 :
- Arduino Alarm Clock Practical Assembly
- Lecture 6 :
- Wireless Power Introduction History and efficiency chart explained
- Lecture 7 :
- How wireless power work
- Lecture 8 :
- Why We need wireless electricity
- Lecture 9 :
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Lecture 10 :
- Range of Witricity and Witricity Applications
Section 10 : Section 10
- Lecture 1 :
- How Safe is Wireless electricity
- Lecture 2 :
- Wireless Powered Arduino Project
- Lecture 3 :
- Let_s Build IT
- Lecture 4 :
- Code and troubleshooting
- Lecture 5 :
- How Does This Circuit Work
- Lecture 6 :
- Course Requirements
- Lecture 7 :
- Download and Install Arduino
- Lecture 8 :
- Assembly
- Lecture 9 :
- The Code
- Lecture 10 :
- Introduction
Section 11 : Section 11
- Lecture 1 :
- How to install Proteous Professional
- Lecture 2 :
- How to Install MikroC Pro for PIC Programming
- Lecture 3 :
- Overivew and The software to be used
- Lecture 4 :
- Compilation Process and Your First C Project
- Lecture 5 :
- How to increase the font size in the Programming environment
- Lecture 6 :
- Why C and Basic Program Structure
- Lecture 7 :
- Variables
- Lecture 8 :
- Statements and Operators
- Lecture 9 :
- LOOP Statements
- Lecture 10 :
- Conditions if and switch
Section 12 : Section 12
- Lecture 1 :
- Numbering System
- Lecture 2 :
- Using Operators
- Lecture 3 :
- Using Functions
- Lecture 4 :
- Digital inputs and Delay loops
- Lecture 5 :
- PIC Manufacture Microship Company
- Lecture 6 :
- Programming PIC and Circuit Prototyping
- Lecture 7 :
- PIC Architecture and PIC Families
- Lecture 8 :
- Harvard Architecture vs Von Neoman Architecture
- Lecture 9 :
- PIC16F84 Microcontrollers Explained
- Lecture 10 :
- Single Word Instructions
Section 13 : Section 13
- Lecture 1 :
- Pin Discription and Ocillator Types
- Lecture 2 :
- System Reset
- Lecture 3 :
- Ports
- Lecture 4 :
- PIC Architecture 2 Ports and Registers
- Lecture 5 :
- Status Register
- Lecture 6 :
- Option Register
- Lecture 7 :
- Banking Mechanism
- Lecture 8 :
- SFRS and GPRS
- Lecture 9 :
- Memory Organization
- Lecture 10 :
- First Project in Proteus
Section 14 : Section 14
- Lecture 1 :
- First Project in MikroC
- Lecture 2 :
- How to deal with PIC Ports + First Code
- Lecture 3 :
- Necessary Connections
- Lecture 4 :
- Simple LED example to get things on the right track
- Lecture 5 :
- Flasher circuit PIC Microcontroller
- Lecture 6 :
- Lighting Led Follower Example
- Lecture 7 :
- Control Led using Push Button
- Lecture 8 :
- Controlling Seven Segment using BCD Counter PIC Microcontroller
- Lecture 9 :
- Controlling LCD using PIC Microcontroller
- Lecture 10 :
- Display and Move Text on LCD
Section 15 : Section 15
- Lecture 1 :
- Stepper Motor Control
- Lecture 2 :
- Dot Matrix Control
- Lecture 3 :
- Keypad Interface and control with PIC Microcontroller
- Lecture 4 :
- Analog To Digital Conversion
- Lecture 5 :
- ADC Module in PIC16F877A
- Lecture 6 :
- ADC Module Configuration Bits and Example
- Lecture 7 :
- Interrupts and External Interrupt Source
- Lecture 8 :
- PortB Line Change Interrupt Source
- Lecture 9 :
- EEPROM Data Write Interrupt
- Lecture 10 :
- Interrupt Handlers and INTCON Register
Section 16 : Section 16
- Lecture 1 :
- Option Register
- Lecture 2 :
- Programming the External Interrupt RBO Example
- Lecture 3 :
- PortB 4 7 Status Change Interrupt
- Lecture 4 :
- RBO and RB4-7 Interrupt Example
- Lecture 5 :
- Serial Communication Introduction and Basics
- Lecture 6 :
- Synchronous Serial Transmission and RS232
- Lecture 7 :
- Essential Concepts in Serial Communication
- Lecture 8 :
- PIC TO PIC And PIC TO PC Communication
- Lecture 9 :
- Serial Communication Example PIC TO PC
- Lecture 10 :
- Timers and Counters
Section 17 : Section 17
- Lecture 1 :
- Timer0 Interrupt
- Lecture 2 :
- Delay Using Timer0
- Lecture 3 :
- Timer0 Interrupt Programming Delay Loops
- Lecture 4 :
- Interrupt Driven Timers
- Lecture 5 :
- Timers0 as a Counter
- Lecture 6 :
- Experiment #4 Some Logic Functions Design
- Lecture 7 :
- Experiment #5 Delay Loops Applications Flasher_Counter_Push Buttons
- Lecture 8 :
- Experiment # 6 7 segment Interface with PIC Microcontroller_Counter Application/
- Lecture 9 :
- Experiment #7 LCD Interface with PIC Microcontroller
- Lecture 10 :
- Experiment #8 Keypad Interface with PIC
Section 18 : Section 18
- Lecture 1 :
- Experiment #9 Analog Digital Conversion
- Lecture 2 :
- Experiment #10 Unipolar Stepper Motor Control
- Lecture 3 :
- Experiment #11 Dot-Matrix Display
- Lecture 4 :
- Experiment #12 Serial Interface with PIC Microcontroller
- Lecture 5 :
- Voltage Current and Resistance
- Lecture 6 :
- Types of current
- Lecture 7 :
- Types of Circuits
- Lecture 8 :
- Volt Ohm Meter Basic
- Lecture 9 :
- Measuring Voltage
- Lecture 10 :
- Measuring Current
Section 19 : Section 19
- Lecture 1 :
- Circuit Diagram Basics and Basic Symbol
- Lecture 2 :
- Introduction To Resistor and Color Band Coding
- Lecture 3 :
- Power Dissipation and Parallel and Series Resistors
- Lecture 4 :
- Ohms Law
- Lecture 5 :
- Introduction To Capacitors
- Lecture 6 :
- Capacitors Behavior and Series and Parallel
- Lecture 7 :
- Introduction to Inductor
- Lecture 8 :
- Introduction to Diode Zener and LED
- Lecture 9 :
- What is 12C
- Lecture 10 :
- Things Your Need to Know about 12C
Section 20 : Section 20
- Lecture 1 :
- Advantages to 12C
- Lecture 2 :
- Disadvantages to 12C
- Lecture 3 :
- 12C Bus Operation
- Lecture 4 :
- Operation Explained in More Details
- Lecture 5 :
- 12C Pins in Arduino
- Lecture 6 :
- Arduino Wire Library 12C Functions
- Lecture 7 :
- Arduino to Arduino 12C Example Circuit Design
- Lecture 8 :
- Arduino to Arduino 12C Example Coding
- Lecture 9 :
- Arduino to DS1307 Time and Date Module Circuit Design
- Lecture 10 :
- I2C Library Routines
Section 21 : Section 21
- Lecture 1 :
- Circuit Design for I2C Testing
- Lecture 2 :
- Coding Simple Example
- Lecture 3 :
- Reading Data from DS1307 Time and Date IC
- Lecture 4 :
- What is SPI
- Lecture 5 :
- SPI Working Principle
- Lecture 6 :
- SPI Library in MikroC Pro IDE
- Lecture 7 :
- Circuit Design
- Lecture 8 :
- Coding
- Lecture 9 :
- Arduino SPI Pins
- Lecture 10 :
- Arduino SPI Library
Section 22 : Section 22
- Lecture 1 :
- Circuit Design Arduino to Arduino SPI Communication
- Lecture 2 :
- Coding Master
- Lecture 3 :
- Coding Slave
- Lecture 4 :
- Introduction to the USB World
- Lecture 5 :
- Advantages of USB Communication
- Lecture 6 :
- USB Pin-out Port Wiring
- Lecture 7 :
- USB Transfer speeds
- Lecture 8 :
- USB Device Classes
- Lecture 9 :
- Introduction to Descriptors
- Lecture 10 :
- Creating a descriptor file in MikroC
Section 23 : Section 23
- Lecture 1 :
- Creating a descriptor file in MikroC - Practical
- Lecture 2 :
- USB Libraries HID Enable
- Lecture 3 :
- USB RAM
- Lecture 4 :
- USB Functions
- Lecture 5 :
- Circuit Design for First Example
- Lecture 6 :
- Installing the Virtual USB Port Feature to enable Simulation
- Lecture 7 :
- First Example Send and Receive Data
- Lecture 8 :
- What is a GUI
- Lecture 9 :
- Microsoft Visual Studio
- Lecture 10 :
- Proteus Virtual USB Installation
Section 24 : Section 24
- Lecture 1 :
- Different Communication Methods that Can be used
- Lecture 2 :
- What is Serial Communication and RS232
- Lecture 3 :
- How To Create Your First GUI Project Quick Intro
- Lecture 4 :
- Circuit Design for Two Leds Controlled by PIC Microcontroller
- Lecture 5 :
- Code Your Microcontroller to Send and Recieve Serial Data
- Lecture 6 :
- Create Your First GUI to Control Two Leds
- Lecture 7 :
- Control PIC Microcontroller using GUI
- Lecture 8 :
- Download and Install Proteus Software
- Lecture 9 :
- Download and Install MikroC Software
- Lecture 10 :
- Download and Install Arduino Software
Section 25 : Section 25
- Lecture 1 :
- Download and Install Fritzing Software
- Lecture 2 :
- Download and Install Microsoft Visual Studio
- Lecture 3 :
- Hardware and Software Requirements
- Lecture 4 :
- What is ESP32
- Lecture 5 :
- ESP Board Overview
- Lecture 6 :
- ESP 32 Pinout v1 DOIT
- Lecture 7 :
- Download and Install Arduino IDE
- Lecture 8 :
- ESP8266 Download and Install Arduino ESP and USB Driver
- Lecture 9 :
- ESP32 v1 Download and Install Arduino Development environment
- Lecture 10 :
- Load your First Code to ESP32 Board
Section 26 : Section 26
- Lecture 1 :
- Blinking a LED
- Lecture 2 :
- Control Built In Touch Sensor with LED
- Lecture 3 :
- Dealing with Analog Signals
- Lecture 4 :
- What is SMTP Server
- Lecture 5 :
- Install ESP32 Mail Library for Arduino
- Lecture 6 :
- Create a New Email Account to be used as Sender
- Lecture 7 :
- SMTP Server Settings
- Lecture 8 :
- Coding the ESP32 Email Alert Project
- Lecture 9 :
- Practical Testing
- Lecture 10 :
- Sensor Alert via Email
Section 27 : Section 27
- Lecture 1 :
- What is a Web Server
- Lecture 2 :
- ESP32 Operating Modes
- Lecture 3 :
- Circuit Design
- Lecture 4 :
- Understanding how esp32 work as a server
- Lecture 5 :
- Coding WiFi and Webserver settings
- Lecture 6 :
- Coding HTTP Requests and Server Start
- Lecture 7 :
- Coding Client Methods
- Lecture 8 :
- Writing HTML Code for Webpages
- Lecture 9 :
- Practical
- Lecture 10 :
- Hosting Your Website
Section 28 : Section 28
- Lecture 1 :
- Creating SQL table
- Lecture 2 :
- PHP Script to Insert Data in Database
- Lecture 3 :
- PHP Script to Display Readings
- Lecture 4 :
- Coding ESP Part2
- Lecture 5 :
- Practical Live Demonstration
- Lecture 6 :
- Add Actual Sensors and display Reading on Webpage
- Lecture 7 :
- What You Will Learn in this Course
- Lecture 8 :
- Software used in this course
- Lecture 9 :
- Download and Install The Software
- Lecture 10 :
- User Interface Quick Introduction
Section 29 : Section 29
- Lecture 1 :
- Practical Work First Experiment Simple Led ONOFF Circuit using switches
- Lecture 2 :
- Flowcharts Introduction and Example
- Lecture 3 :
- Flowcharts Subroutine Example
- Lecture 4 :
- Flowcharts and Microcontrollers Intro
- Lecture 5 :
- 7 Segment Counter Example
- Lecture 6 :
- Using 3D Multimeter and Graphs for Circuit Testing
- Lecture 7 :
- Mechanism and Mechanical Parts
- Lecture 8 :
- Download and Install Simulation Software
- Lecture 9 :
- Interface Explained
- Lecture 10 :
- Interface Menu Explained in Details
Section 30 : Section 30
- Lecture 1 :
- Main Window Commands
- Lecture 2 :
- Simulation Boards MCLab1 For PIC16F84, PIC16F628 or PIC16F648
- Lecture 3 :
- Simulation Boards PIC Genios Board and Arduino Board
- Lecture 4 :
- Playing with Code Examples with Different Compilers
- Lecture 5 :
- Buttons and LEDs Reading Input and Writing Output
- Lecture 6 :
- LCD Interfacing and Simulation
- Lecture 7 :
- Relay Interfacing with PIC Microcontroller
- Lecture 8 :
- 7 Segment Simulation
- Lecture 9 :
- Buzzer Temperature Fan Heater and PWM Simulation Components
- Lecture 10 :
- Download And Install Software Free
Section 31 : Section 31
- Lecture 1 :
- Getting Started
- Lecture 2 :
- Customizing Parts
- Lecture 3 :
- Schematic
- Lecture 4 :
- Exporting your design as Image or PDF
- Lecture 5 :
- Making PCB Part1
- Lecture 6 :
- Making PCB Part2
- Lecture 7 :
- Cleaning Board
- Lecture 8 :
- Finishing Board and Making it yours
- Lecture 9 :
- Making a more advance random schematic design
- Lecture 10 :
- Print PCB Design on Heat Paper
Section 32 : Section 32
- Lecture 1 :
- PCB Board Cleaning and Etchin
- Lecture 2 :
- Drilling
- Lecture 3 :
- What You will learn
- Lecture 4 :
- Introduction Prestart Definitions
- Lecture 5 :
- Installing the Required Software Proteus
- Lecture 6 :
- Basic introduction to Proteus ISIS interface and Tools
- Lecture 7 :
- Design Draw and Test your First Simple Circuit
- Lecture 8 :
- Introducing Some Techniques to Master ISIS
- Lecture 9 :
- Create Your Own Electric Element in ISIS Proteus
- Lecture 10 :
- Design Draw and Test a more advanced Circuit
Section 33 : Section 33
- Lecture 1 :
- Basic Introduction to ARES interface and tools
- Lecture 2 :
- Preparing ISIS Circuit Design to be moved to ARES
- Lecture 3 :
- Placing Elements the right way in ARES
- Lecture 4 :
- Start Routing in Different Ways
- Lecture 5 :
- Finalize Your Circuit for mass production
- Lecture 6 :
- Printing Your design on Heat paper
- Lecture 7 :
- Course Contents
- Lecture 8 :
- How to Solder
- Lecture 9 :
- Things you need to start soldering
- Lecture 10 :
- Things to Consider when Choosing Soldering Irons
Section 34 : Section 34
- Lecture 1 :
- Soldering Accessories
- Lecture 2 :
- Soldering Steps Step One Preparation
- Lecture 3 :
- Soldering Steps Step Two Tinning
- Lecture 4 :
- Soldering Steps Step Three Soldering
- Lecture 5 :
- Tips and Tricks
- Lecture 6 :
- Examples of Bad Soldering
- Lecture 7 :
- Practical Example of Good soldering and Bad soldering
- Lecture 8 :
- Practical Soldering Iron Practical
- Lecture 9 :
- Lets Try Soldering
- Lecture 10 :
- Cleaning Your Soldering Iron
Section 35 : Section 35
- Lecture 1 :
- Practical How to clean soldering tip
- Lecture 2 :
- Practical How to solder correctly
- Lecture 3 :
- Practical Soldering
- Lecture 4 :
- What is a Training Kit
- Lecture 5 :
- How training kits make your programming, wiring and testing an easy job
- Lecture 6 :
- What are the main components that must be in the training kit
- Lecture 7 :
- What are the extra components that you can be added
- Lecture 8 :
- What is Printed Circuit Board Design
- Lecture 9 :
- What is the best software to do that
- Lecture 10 :
- How to start Designing your kit
Section 36 : Section 36
- Lecture 1 :
- Adding power circuit with protection
- Lecture 2 :
- Making PCB Part1
- Lecture 3 :
- Making PCB Part2
- Lecture 4 :
- Final PCB
- Lecture 5 :
- Finishing the board
- Lecture 6 :
- Buying items online and End of the Course
- Lecture 7 :
- Installing Arduino Library For Proteus
- Lecture 8 :
- Downloading and Installing Proteus Software
- Lecture 9 :
- Adding Arduino Library to Proteus
- Lecture 10 :
- Downloading and Installing Arduino Coding Software
Section 37 : Section 37
- Lecture 1 :
- Your First Code in Arduino Coding Software
- Lecture 2 :
- Editing the code and Getting the Hex File
- Lecture 3 :
- Load the hex file and Run the Simulation
- Lecture 4 :
- Download and Installing Altium Designer
- Lecture 5 :
- Altium Designer Interface Introduction
- Lecture 6 :
- Create Component Symbol _ Add Pins
- Lecture 7 :
- Finishing the Schematic
- Lecture 8 :
- Creating Your Componenets Symbol - Making Footpring and PCB Layout
- Lecture 9 :
- Link footprint with Schematic Library
- Lecture 10 :
- Adding the new Library File to your Design
Section 38 : Section 38
- Lecture 1 :
- Creating the Atmega Component Symbol
- Lecture 2 :
- Creating the Atmega PCB Footprint
- Lecture 3 :
- Adding Components and Placing them on Schematic
- Lecture 4 :
- ATMEGA Schematic Connection
- Lecture 5 :
- USB Connector Schematic
- Lecture 6 :
- Header Pins for Nano Board
- Lecture 7 :
- Adding Resistors LED Indicators Voltage Regulator
- Lecture 8 :
- Annotating and Compiling Project
- Lecture 9 :
- Getting Started with the PCB Design Solve Errors
- Lecture 10 :
- Drawing The Board Shape
Section 39 : Section 39
- Lecture 1 :
- Placing PCB Items Atmega and Headers
- Lecture 2 :
- ICSP SWITCH Resistor array crystal microusb
- Lecture 3 :
- FTDI Regulator Capacitors
- Lecture 4 :
- Manual Routing
- Lecture 5 :
- AutoRouting
- Lecture 6 :
- How to make the autorouting work for you
- Lecture 7 :
- Improve AutoRouting Trial and Error
- Lecture 8 :
- Greber File and Bill of Material
- Lecture 9 :
- Introduction and Required Components
- Lecture 10 :
- Schematic
Section 40 : Section 40
- Lecture 1 :
- Download and install Pinguino IDE
- Lecture 2 :
- Download Bootloader File
- Lecture 3 :
- Burn Hex File of Bootloader to Microcontroller
- Lecture 4 :
- Drivers
- Lecture 5 :
- First EXAMPLE Blink A LED
- Lecture 6 :
- Now Build your own Pinguino
Our learners work at
Frequently Asked Questions
How do i access the course after purchase?
It's simple. When you sign up, you'll immediately have unlimited viewing of thousands of expert courses, paths to guide your learning, tools to measure your skills and hands-on resources like exercise files. There’s no limit on what you can learn and you can cancel at any time.Are these video based online self-learning courses?
Yes. All of the courses comes with online video based lectures created by certified instructors. Instructors have crafted these courses with a blend of high quality interactive videos, lectures, quizzes & real world projects to give you an indepth knowledge about the topic.Can i play & pause the course as per my convenience?
Yes absolutely & thats one of the advantage of self-paced courses. You can anytime pause or resume the course & come back & forth from one lecture to another lecture, play the videos mulitple times & so on.How do i contact the instructor for any doubts or questions?
Most of these courses have general questions & answers already covered within the course lectures. However, if you need any further help from the instructor, you can use the inbuilt Chat with Instructor option to send a message to an instructor & they will reply you within 24 hours. You can ask as many questions as you want.Do i need a pc to access the course or can i do it on mobile & tablet as well?
Brilliant question? Isn't it? You can access the courses on any device like PC, Mobile, Tablet & even on a smart tv. For mobile & a tablet you can download the Learnfly android or an iOS app. If mobile app is not available in your country, you can access the course directly by visting our website, its fully mobile friendly.Do i get any certificate for the courses?
Yes. Once you complete any course on our platform along with provided assessments by the instructor, you will be eligble to get certificate of course completion.
For how long can i access my course on the platform?
You require an active subscription to access courses on our platform. If your subscription is active, you can access any course on our platform with no restrictions.Is there any free trial?
Currently, we do not offer any free trial.Can i cancel anytime?
Yes, you can cancel your subscription at any time. Your subscription will auto-renew until you cancel, but why would you want to?
Instructor

12880 Course Views
124 Courses



 Tech & IT
Tech & IT
 Business
Business
 Coding & Developer
Coding & Developer
 Finance & Accounting
Finance & Accounting
 Academics
Academics
 Office Applications
Office Applications
 Art & Design
Art & Design
 Marketing
Marketing
 Health & Wellness
Health & Wellness
 Sounds & Music
Sounds & Music
 Lifestyle
Lifestyle
 Photography
Photography